Slips, Trips and Falls Safety Talk

Introduction to Workplace Safety
Earlier this year, OSHA issued a $1 million dollar fine against a construction company for repeated failure to provide fall protection. Falls remain one of the leading causes of workplace fatalities, yet are preventable. With the proper training and information, workers can significantly reduce their risk, and businesses can avoid significant fines.
That’s why in this article, we’ll dive into the most common causes of slips, trips, and falls; and uncover actionable strategies you can implement to mitigate risks for your teams.
What industry is the most prone to slips, trips and falls?
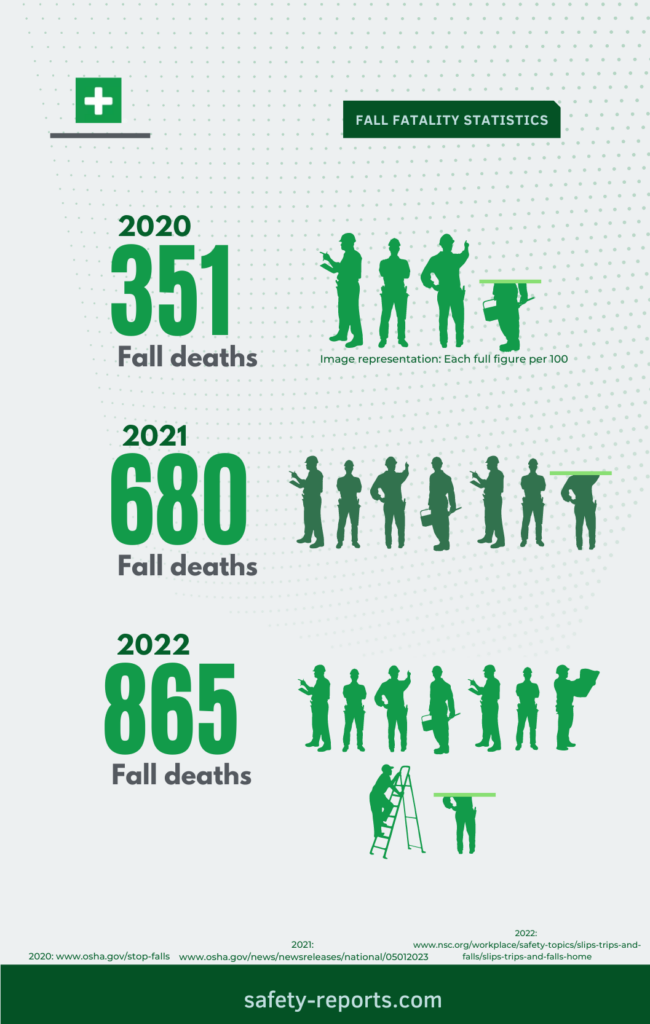
The construction industry is most at risk for fatal falls. More than seven times the rate of other industries according to NSC. In 2021, nearly 1 in 5 workplace deaths occurred in the construction industry with most falls occurring to a lower level.
Falls are the most common hazard and leading cause of death in construction. They make up a part of OSHA’s “Fatal Four” and OSHA offers lesson plans that focus on each topic tailored to the industry.
Why Prevention is Crucial
Accidents resulting from slips, trips, and falls are among the most frequent and severe workplace injuries. According to the National Safety Council, they account for over 30% of all workplace injuries. For businesses, these incidents can lead to increased insurance premiums, legal fees, and lost productivity.
Beyond the numbers, there’s a moral responsibility to ensure the well-being of staff. Preventing such accidents promotes a culture of care and safety, which can also improve employee morale and satisfaction. A safe workplace is a productive one, and taking proactive steps to prevent accidents is both a wise and ethical choice.
Common Causes of Slips, Trips and Falls
 Wet and Uneven Surfaces
Wet and Uneven Surfaces
One of the primary causes of slips and falls is wet or uneven surfaces. This can include everything from freshly mopped floors to unexpected patches of ice or snow at building entrances. Surfaces that are not level, such as loose floorboards or uneven tiles, can also be hazardous.
For example, consider a warehouse where spills happen frequently. If these spills aren’t cleaned up promptly, employees are at risk of slipping. Similarly, construction sites often pose trip hazards due to the nature of the work environment.
Clutter and Obstructions
Another common culprit is workplace clutter. Items left in walkways, electrical cords stretched across rooms, and poorly arranged furniture can all create dangerous trip hazards. In busy environments, such as offices or hospitals, clutter can quickly become a serious issue.
Imagine a busy job site where toolboxes or any other equipment is set down. A worker walking through who is carrying materials or equipment themselves could easily trip over these obstacles, leading to potential injury. It’s important to keep pathways clear and organized to prevent such incidents.
Poor Lighting
Adequate lighting is crucial for safety. Dimly lit areas can obscure potential hazards, making it difficult for employees to see and avoid them. Poor lighting is especially dangerous in stairwells, storage rooms, and areas with heavy foot traffic.
Think about a poorly lit parking structure or garage. Without proper illumination, employees may not see oil spills or uneven pavement, increasing the risk of an accident. Ensuring that all areas are well-lit can significantly reduce these risks.
Best Practices for Prevention
Consistent maintenance and housekeeping are key to preventing slips, trips, and falls. This includes promptly addressing spills, repairing damaged flooring, and removing clutter from walkways. Regular inspections can help identify potential hazards before they cause accidents.
Practices for fall prevention include:
- Implementing a daily cleaning schedule
- Inspecting for floor damage, loose tiles, or any hazardous clutter or debris
- Enforce fall protection systems such as harnesses
- Safety training and emergency preparedness
- Ensure safe access to all work areas using stable ladders, scaffolds, etc.
- Use safety nets where applicable
- Consistent supervising and monitoring of risky work
- Conduct regular safety audits and improve measures and practices
Proper Signage and Warnings
Signage plays a vital role in alerting employees to potential hazards. Using clear, visible signs to indicate wet floors, uneven surfaces, or areas under maintenance can help prevent accidents. Temporary signage should be used during cleaning or maintenance activities.
Consider a construction site where water is sprayed for dust control. By placing “Wet Floor” signs in visible areas where employees and clients are likely to slip and fall can reduce risk.
Appropriate Footwear and Equipment
Encouraging the use of appropriate footwear and safety equipment can significantly reduce the risk of slips, trips, and falls. Non-slip shoes, for example, are designed to provide better traction on slippery surfaces.
In construction, workers using proper footwear and helmets are better protected against falls and other injuries. Job sites often have heavy objects, tools, and various other hazards that can all be resolved with shoes that have the following traits:
- Impact protection
- Puncture and tear resistance
- Slip resistance
- Electrical hazard protection
- Ankle support
- Comfort and material longevity
The Role of Employee Training
Employee training and awareness programs are essential for fostering a safety-conscious culture. Regular training sessions can educate staff about potential hazards and how to avoid them. OSHA has a wide variety of safety training topics to choose from, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive safety education.
But the best trainings are interactive. Interactive workshops and real-life scenarios can make these sessions more engaging and effective.
For example, a manufacturing plant might conduct monthly safety drills to train employees on how to handle spills and obstructions. These drills can increase awareness and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
There are numerous ways to make your safety trainings engaging. Employers can include hands on activities, start group discussions, and more to make the experience fun and memorable.
To ensure you workers are getting all necessary training, employers should track training progress and document toolbox talks using the Safety Reports safety training app. This app will improve your company’s safety program with a variety of features including preloaded safety talks and attendance verification.
Encouraging Reporting
Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting hazards is crucial. Encourage staff to report spills, damaged flooring, or poorly lit areas without fear of retribution. Implementing a simple reporting system can make this process easier.
In an office setting, a simple online form for hazard reporting can empower employees to take an active role in maintaining a safe workplace. Promptly addressing reported hazards demonstrates a commitment to safety.
Continuous Education
Safety training shouldn’t be a one-time event. Continuous education and refresher courses can keep safety top-of-mind. Regular updates on new safety protocols and technologies can help staff stay informed and prepared.
Hold A Safety Stand-Down
What is a safety stand down?
A safety stand down is a company-wide event used by employers to educate and inform employees about important safety topics such as fall prevention.
Here are some tips for topics to address in a safety stand down.
- Conduct safety equipment inspections.
- Talk about or develop rescue/action plans with your team for when injuries take place.
- Talk about PPE and other safety equipment essentials.
By holding a Safety Stand-Down, companies can receive a Certificate of Participation from OSHA. This certificate recognizes the time and effort devoted to preventing falls with work crews.
Conclusion
Preventing slips, trips, and falls in the workplace is a continuous effort that requires attention to detail and a commitment to safety. By understanding common causes, implementing best practices, and leveraging technology, businesses can create safer work environments.
Remember, a safe workplace doesn’t just happen—it’s built through consistent efforts and a proactive approach. By prioritizing safety, companies can protect their most valuable asset—their people.

 Wet and Uneven Surfaces
Wet and Uneven Surfaces

